随着科技发展,人类对能源的需求与日俱增,而目前商业化的锂离子电池(理论容量372mAh/g)已不能满足该需求,高容量密度电池的开发已成为研究热点。
锂金属具有高理论比容量(3860mAh/g),在储能领域有很大应用潜力。然而锂枝晶的生长,不仅降低了电池性能,而且容易发生短路,造成安全隐患。这些问题严重阻碍了锂金属电池的发展和实际应用。
为解决上述问题,科学家们提出了各种方案,如制备三维嵌锂基体、锂金属表面包覆、隔膜改性等。但这些方式增加了电池整体重量,且制备过程繁琐,不利于商业化生产。
最近,Qian等通过对比不同电解液环境对锂枝晶生长的影响,提出高浓度LiFSI醚类电解液环境下,即使没有嵌锂基体,仍可有效抑制锂枝晶在铜集流体上的生长,同时,电池库伦效率也有显著提高。
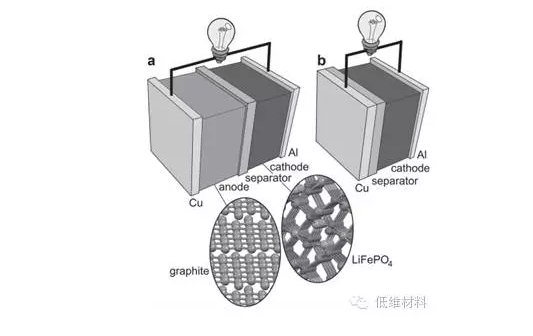
Figure 1. Schematicillustrations of battery configurations. a) State-of-the-art Li-ion battery,i.e., Cu|C6||LiFePO4|Al. b) Anode-free battery,i.e.,Cu||LiFePO4|Al.
实验以Cu-LiFePO4电池为研究体系,分别选用1 M LiPF6-EC/DMC(1/2 v/v)酯类电解液和4 MLiFSI-DME醚类电解液进行对比。实验结果表明随着循环次数增加,酯类电解液环境下电池电阻增加明显,而4 MLiFSI-DME醚类电解液环境下,电阻增幅较小。
而且在4 MLiFSI-DME环境下,多次循环后平均库伦效率大于99%。即使在2 mA cm-2电流密度下,库伦效率仍接近100%。
另外,该研究发现通过调节测试条件,也可提高库伦效率。当锂以0.2 mA cm-2沉积,2mA cm-2脱出时,平均库伦效率可达99.6%,高于一直以0.2 mA cm-2/2mAcm-2进行循环的库伦效率。
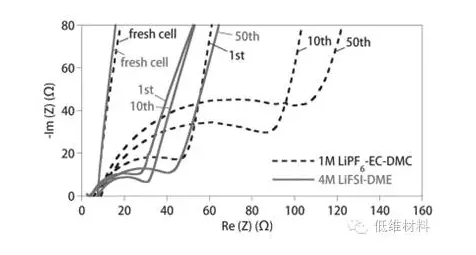
Figure 2. Nyquistplot of anode-free Cu||LiFePO4 cells with either 1 M LiPF6-EC/DMC(dashed line) or 4 M LiFSI-DME (solid line) after differentcycles whencharged/discharged at 0.2 mA cm?2. All data were collectedatdischarged state of the cells.
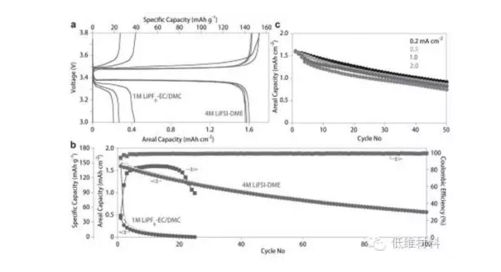
Figure 3. Electrochemical performance of anode-freeCu||LiFePO4 cells with either 1 M LiPF6-EC/DMC or 4 M LiFSI-DME.a) Charge/discharge voltageprofiles for the first three cycles with the twoelectrolytes. b) Capacity retention and CE of the cells with the twoelectrolytes as a function of cycle numberwhen charged/discharged at 0.2 mA cm?2(open symbols: charge capacity, filled symbols:discharge capacity). c) Capacityretention of the cells with 4 M LiFSI-DME charged/discharged at differentcurrent densities.
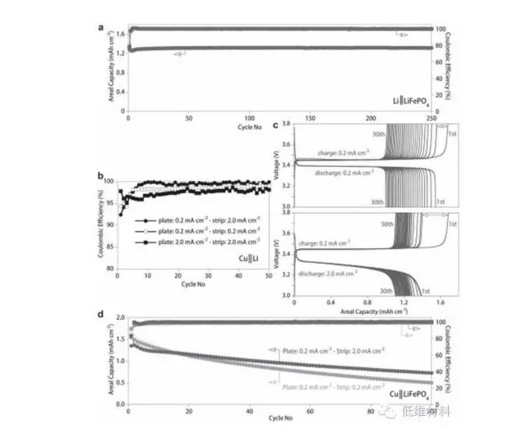
Figure 4. Cycling performance of Cu||Li and Cu||LiFePO4cells with 4 M LiFSI-DME cycled at different current densities. a) Li||LiFePO4cell cycled withlow-rate (C/5) charging and high-rate (2 C) discharging. b) CEof Cu||Li cells. A capacity of 0.5 mAh cm?2 was used to plate the Limetal, which wassubsequently stripped by cycling to 1.0 V versus Li/Li+.c) Charge/discharge voltage profiles for the first 30 cycles of the anode-freecells (Cu||LiFePO4)with 4 MLiFSI-DME cycled at different currentdensities. d) Discharge capacity and CE of anode-free Cu||LiFePO4cells charged at 0.2 mA cm?2 anddischarged at either 0.2 or 2.0 mAcm?2 (open symbols: charge capacity, filled symbols: dischargecapacity).
综上,该工作提出了一种可有效抑制锂枝晶生长的电解质,并通过表征解释其原因,对锂金属电池的研究和大规模生产具有指导意义。
相关研究成果发表在著名刊物Advanced Functionalmaterials上(DOI:10.1002/adfm.201602353.) JiangfengQian, Brian D. Adams, Jianming Zheng,Ji-Guang Zhanget al. Anode-Free RechargeableLithium Metal Batteries.Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016.)。

